What is an organization? What are it's fundamental components?
Organization Fundamentals
What is an organization?
Organizations are social systems that are created to fulfill certain well defined goals; they have a formal structure to facilitate efficient internal coordination and to be able to respond to the external environment.
System: Organizational system consists of various interacting components (people/resources) that acquire inputs (goals) from the external environments, processes them (structure & processes) and produces an output (product/service) to be consumed back by the external environment (customers).
Organizations can be either closed or open system. A closed system organization is the one that is self-sufficient and its operations are not influenced by external influences like competition, economy, suppliers or external resources. However such autonomous entities that are isolated from outside ideally do not exists. The closed form of close-systems can be found only in government funded initiatives like space and defense organizations which are not much influenced by changes in Govt. or economy.
Open Systems are tightly coupled with the external environment; their survival depends upon how quickly they anticipate external changes and how impeccably they adapt to them. Since the internal efficiency and innovation is just one aspect, the open systems are highly complex and intensely challenging. Just like biological species become extinct it they are unable to adapt and process the external changes, so are the modern organizations.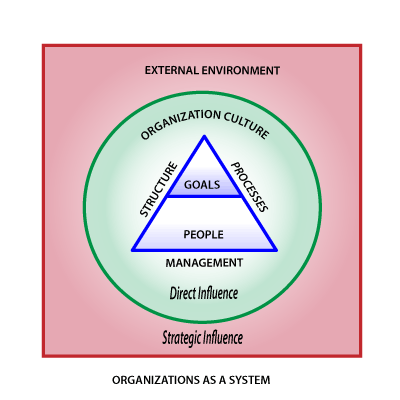
Goals: An organization exists to satisfy certain goals or vision of its establishing leaders. The organization can either be established for purpose of making profit, like most of the business organizations. Or it can be a non-profit organization that is motivated to create a social impact instead of profit, like non-government organizations (NGOs). In general, the organizations are established to facilitate innovation and to produce goods or services more efficiently.
People: Organizations are made up of people and the interactions or communication between them is the key to organization’s effectiveness. Thus organizations are the most significant social systems in people’s lives if measured in terms of amount of time spent in individual’s life.
Structure: The organization structure designates the hierarchy and formal reporting relationships between managers and subordinates. Organizations are often subdivided into smaller departments or functional units, depending upon the size and maturity levels. The structure of the organization governs how all its components interact with one another and is designed to effectively & efficiently meet its objectives.
Processes: The organization’s rules and policies, performance evaluations, recruitment and retention are some formalized processes that help manage the organization in predictable manner.
Culture: In an organizational system, the goals, resources and people are structured and then managed through some processes and leadership. This gives birth to the culture of an organization, which are the unwritten values, rules and beliefs that are shared between all the members of the organization. The leadership has a direct influence upon the culture of an organization, leaders use their authority to change its structure, their charisma to boost the motivation, their vision to establish the goals and their skills orchestrate its smooth operations.
External Environment: It’s the collection of all the elements that have potential to influence whole or some part of the organization, the organization must be sensitive to external environments demands and must be able to respond to them in order to survive. The customers, suppliers, competitors, labor market & federal laws, finance, recession, technology, acquisitions etc are all examples of the external environment. The organizational leaders do not have direct control over the external environment, but can influence or respond to it by deploying various strategies.
Evolution of organizations
Pre-industrial era: In the pre-industrial era, organizations predominantly existed under the administration of the kings and were governed by kings appointed ministers. Most of the goods were produced by individual craftsmen who worked under other leading craftsman; there existed no formal organized form of production of the consumer goods.
Industrial Revolution: However, the industrial revolution gave birth to factories and manufacturing units that employed a large number of manpower leading to the need to have a formal structure and control to ensure their efficient functioning. The organizations at this stage largely consisted of trained and skills workers who were directed by highly educated managers and leaders. Blue-collar workers are usually distinguished from there superiors based on their education level.
Information age: With advent of the information age, high availability and demand of well educated workers, there exists little educational difference between the managers and the employees. This poses a new challenge for the leadership; traditional hierarchical organizational structures often prove de-motivational due to lack of acceptance of the authority. The learning organizations, which are based on horizontal collaborations, while maintaining the individual’s organizational identity, are being touted as more effective and satisfying styles.
