Explains the two leadership styles, "People oriented" Vs "Task Oriented" using the Blake and Mouton's Leadership Grid.
Leadership Style
The leadership style is determined by the approach a leader takes for getting things done. Since the primary role of a leader is to get the tasks done through the people, leaders have to focus on the productivity of the employees along with maintaining good relationship with them.
Leaders who are strong in technical skills would naturally focus on structuring and planning of the work, defining activities and scheduling them. On the other hand, leaders who have strong personal traits would focus on building trust, delegating responsibilities and thereby bringing meaning to their work and motivating them. These two distinct styles are termed as “task-oriented style” or “people-oriented style” of leadership.
Are there leaders who use both these styles simultaneously? The early researcher (Michigan) concluded that these two traits are mutually exclusive with one another; a leader might only posses either one of them but not both. However later research showed that these two independent orientations exists with different degrees in leaders.
Blake and Mouton’s Leadership Grid
The leadership grid proposed by Blake and mouton (1964) attempts to conceptualize how the “task” and “people” orientation of a leader, helps the organization in attaining it’s purpose. The leadership grid joins the “task concern” along the horizontal axis and “people concern” along the vertical axis.
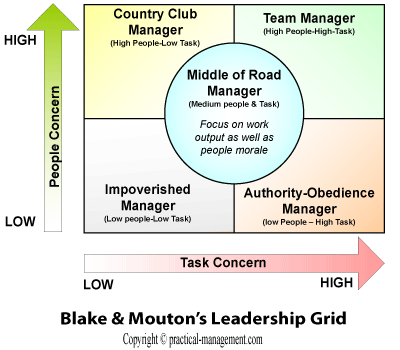
Depending upon the scale of concern of each axis, the grid categorizes the leadership into five distinct styles:-
- Impoverished Manager (Low People - Low Task Concern). Such leaders exhibit lack of concern for the result of the assigned task or interpersonal relationship. They act uninvolved and withdrawn from the organizations objectives and often give an impression of incumbency. However, one ponders how do such leaders rise to their present position? Is their style a suggestion of lack of motivation, saturation of position in organization or something else? Since it might appear that they perform only to sustain their employment.
- Country Club Manager (High People – Low Task concern). Such leaders exhibit care and concern for the people, they create a comfortable and friendly environment while de-emphasizing the productivity of task. In certain situations, like a country club manager, where the primary role is to create a comfortable environment for clients while providing routine amenities, such leaders might be desired.
- Authority Compliant Manager (Low People – High Task concern). These leaders have a strong focus on good planning and successful completion of task. They place little emphasis on relationships, motivation or communication with their subordinates. They believe in setting up the organizational structure that maximizes the productivity while minimizing the interference of human elements. At first, it might appear to be an undesired style of leadership, since it is very dictatorial, but such leaders are highly effective in tasks that are extremely critical, highly structured and have a short duration. An organization at the verge of collapse might require such leader to fix it, but might not be suitable once the restructuring is finished and organization is back to routine.
- Middle-of-the-Road Manager (Medium People & Task concern). These leaders are compromisers who have weak balance between concern for people and task. They avoid any conflicting situations and try to get the work done by moderately focusing on interpersonal relationships, they do not try to push others too much for sake of better results. Such managers can be effective in matured and structured organization that is performing routine job functions or services and do not envision much growth in future.
- Team Manager (High People – High Task concern). This style tries to maximize the concern for both task and people. Such leaders create strongly structured tasks, set clear priorities and track the progress on timely basis. At the same time, they promote active participation & teamwork, creates open and comfortable environment, sets guidelines for effective communication and empowers the individuals enough to keep them motivated. Even though this is the most preferred style, it may be best suited in a growing organization which needs to thrive on internal synergy.
Style Variants
Each leader usually has one of the above dominant leadership style, it comes naturally and is most comfortable for the leader. However, leaders do adapt their styles according to situations, the kind of task, it’s urgency and complexity, competence and morale of the team etc. Variations of styles in a leader makes them unpredictable to the team, they might be perceived as leaders who are opportunistic, acts gracious only for their selfish interest. In a long run, they do loose their credibility and trust.
Strengths of Style Approach
- Style approach shifts the focus from personality traits and skills to how leaders behave in different situations.
- It is centered around two basic orientations, task vs people, which are very intuitive and it’s easy to conceptualize various variations of them.
General Criticism of Style Approach
- Style approach also fails to prove the effectiveness of task vs people behavior in the outcome of leadership.
- Even though the style approach prefers “team manager” style as the most desirable, other styles are also effective in different situations.
