The most fundamental role of a leader is to define the organizational goal, formulate plans and organize people to achieve the goals through the execution of plans.
Role of an Organizational Leader
What is leadership?
“What makes a leader?” has been a key question asked throughout the organizations of this century. Although there is a tremendous research in the subject, however no clear blueprint of effective leadership has emerged that strongly relates to the success in variety of organizations.
General Electric Corporation defined, "a leader is considered to be someone with vision and ability to articulate that vision to the team, so vividly and powerfully that it becomes their vision".
Another text defined, "a leader is someone who brings to the situation a clear and compelling sense of the future as well as an understanding of the actions needed to get there successfully."
There are as many definitions of leadership as there are people who have attempted to define it. Thus defining leadership is perhaps a futile exercise since it remains open to multiple interpretations by different individuals.
However, a more rational way to comprehend leadership is to focus on a particular framework, like an organization and try to define the expected role of a leader.
What is the role of a leader in an organization?
The most fundamental role of a leader is to define the organizational goal, formulate plans and organize people to achieve the goals through the execution of plans.
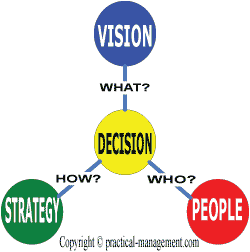
The figure illustrates the 3-Dimensions of leadership tasks
- Vision - It defines the purpose, or simply “What to do?” A vision includes determining the next product or feature, finding new markets for the product, adoption of new technology etc.
- Strategy - It articulates the plans, “How to achieve the vision?” Plans or strategies demonstrate the job knowledge or the skills of a leader. It includes restructuring organization, product management, strategic management etc.
- People - “Who should carry out the Strategy?” How to make people accomplish the strategy and hence the goal, The people skills include providing inspiration & motivation, establishing relationship, intelligently using power and position of leadership etc.
The most important skill that bridges the three job functions is “making decisions”. Any leader has to deal with array of options in his every day chore; a good leadership depends on how effectively he chooses those alternatives. Hence effective decision making is an essential skill for any leader, fortunately a lot of research and academics have focused on this area and there are substantial materials and tools for it.
Transient state of leadership roles
Any organization goes through a series of evolutionary changes depending on various external and internal factors. Take the example of auto industry, when the gas is cheap, the industry focuses on trendy, spacious automobiles. But as gas becomes expensive, the industry shifts it’s vision towards more fuel efficient vehicles.
Similarly a technology start-up company requires task-oriented leaders and essentially hires employees with high experience who can be delegated with various tasks. However, once the company grows in size many folds, the same leaders become ineffective since the organization has now a lot of fresh young graduates who require substantial coaching, need for people skills in the leaders become more prominent.
Hence it is pretty clear that leaders have to adapt to the changes in the organization and their roles keep on changing. A solutions that may apply at a particular given time and situation may not be applicable at a later time. In fact, every leadership style or solution has certain period of effectiveness, after which it changes the problem itself to a new state requiring a different approach. This also explains why some leaders who were very effective in an organization in one era become obsolete later.
The following table illustrates the transition of leadership roles due to different transformational factors over a course of time.
|
State1 |
Transformation Factors |
State2 |
|
Vision1 |
Competition -growing or shrinking Economy- rising or falling Technology - new, cost effective |
Vision2 |
|
Strategy1 |
Vision Organizational changes
|
Strategy2 |
|
Organization1 |
Recruitments or layoffs Maturity Re-organization |
Organization2
|
